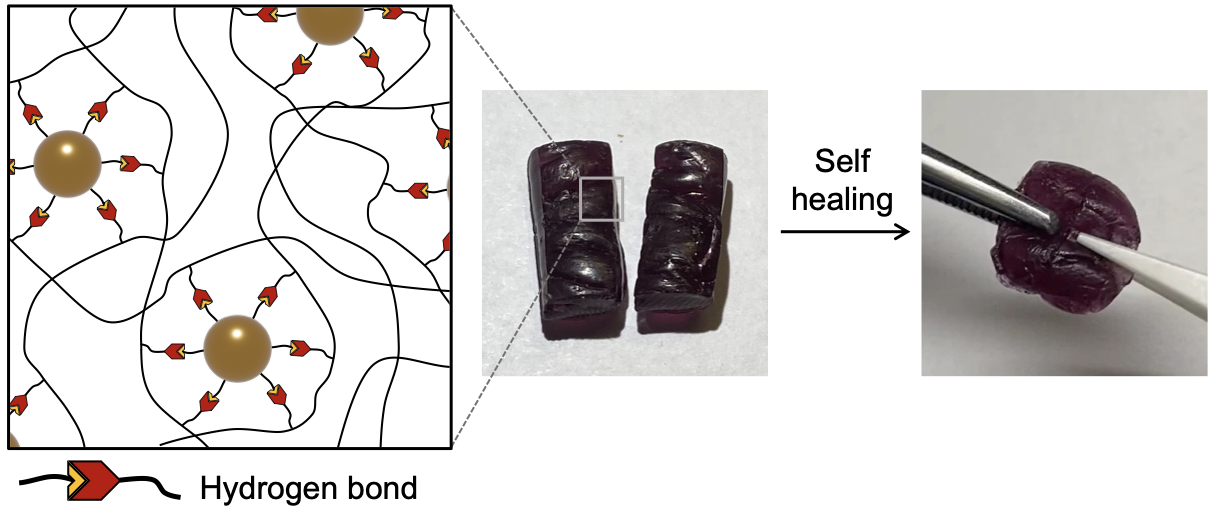
Polymer Nanocomposites Crosslinked using Nanoparticle-Based Bonds
Given increasing environmental issues related to plastic materials, the idea of replacing polymer networks formed via covalent bonds with non-covalent bonds remains a research area of significant promise. Physical interactions in polymer networks enable materials to be easily remolded, self-healed, and recycled on demand due to rapid bond exchange, but these materials typically exhibit reduced mechanical properties compared to ones that are chemically crosslinked. Despite many benefits, this makes self-healing materials unsuitable for many applications. Therefore, materials that can dynamically change their mechanical property in response to stimuli are ideal. We use photo-responsive nanoparticles as particle-based crosslinks to generate a mechanically robust polymer network with tunable bond exchange rate. This research aims to gain a fundamental understanding of the effects of polyvalent interactions, strength of interactions, and nanoparticle concentration and size on crosslinking mechanism and network properties.


